- Medical catalog
- Industrial catalog
By manufacturer
TechnologiesA CELL OR AN ACCUMULATOR?
A cell is designed for single-use only and therefore cannot be used once it has run flat.
An accumulator can be recharged between 500 and 1,000 times depending on the technology and the application in question. It is therefore more expensive to purchase but much more economical and ecological than a cell.
MOST COMMONLY USED TYPES OF CELLS AND ACCUMULATORS:
CELLS
Saline: 1.5V. These cells are not very powerful and are adapted to intermittent uses that do not require a powerful charging current.
Alkaline: 1.5V. Alkaline cells have a greater energy density and longer lifespan than saline cells.
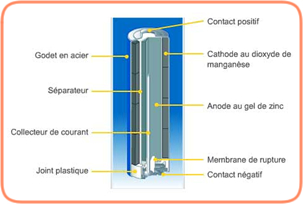
Lithium: 1.5V – 3V – 3.6V. Lithium cells have a much longer lifespan than traditional cells. They are recommended for high-consumption applications such as flashes and digital cameras.
The lithium-manganese pair (Li-MnO2) is the most used. They are found in mass market applications (button cells, photo cells, etc.). The lithium-thionyl chloride pair (Li-SOCl2), 3.6V, is more adapted for professional use.
ACCUMULATORS
Lead: 2V – 4V – 6V – 12V – 24V. The lead-acid accumulator is the oldest of current technologies. Recycling of lead batteries is well established.
There are two types of lead batteries:
- Vented lead: liquid electrolyte
- Sealed lead: AGM, gel
You should always bear in mind that the two main causes of death from a lead accumulator, irrespective of its type, are full-discharging and over-charging.
You must therefore never discharge a lead accumulator below 1.65V per element (or 0V for a 12V battery). Below this, destruction of the accumulator is certain.
Neither must you overcharge a battery by leaving it at 2.35V (14V for a 12V battery) for more than 20 hours (where the battery is empty at the time charging is set).
A lead battery is charged at a constant voltage (2.27V/elt).
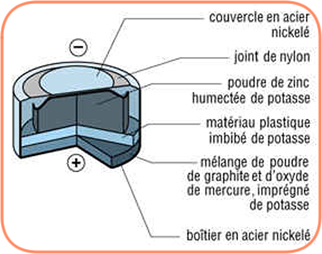
NiCd: 1.2V. A few years ago, these accumulators were the most widespread amongst portable devices from GSM to digital cameras, to wireless drills, to camcorders. Today, the NiCd accumulator is mainly found in industrial applications. There is a wide range of cells on the market (format and capacity) used to manufacture batteries from 2.4V to more than 48V.
The NiCd battery is charged at a constant voltage.
NiMh: (Nickel Metal-Hydride)
1.2V. This technology is present in a wide range of domestic and industrial products.
From an environmental point of view, the advantage of NiMh batteries is that they do not contain cadmium or lead, which are both highly polluting.
Moreover, they are more efficient and do not have a memory effect.
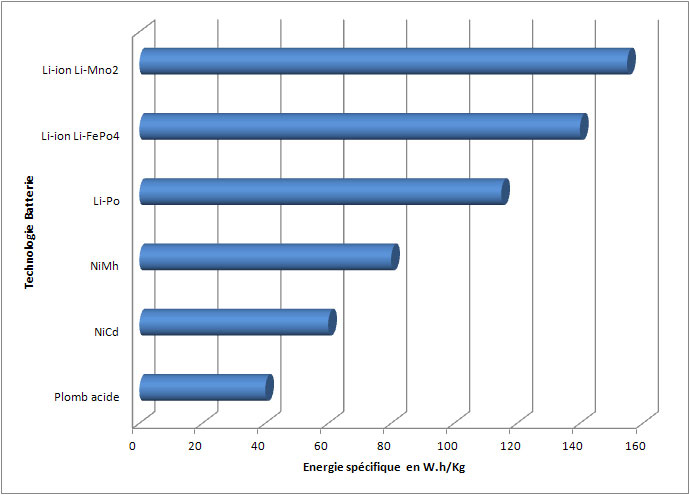
Li-Ion (Lithium-Ion)
3.6V – 3.7V. Lithium-Ion batteries will successively replace all other technologies. They have a high energy capacity (twice that of NiMh) and can be recharged quickly. This technology has replaced NiMh in all general public applications (telephones, computers, etc.)
To prevent spontaneous ignition, this technology requires electronic monitoring, a type of fuse that limits charge and discharge voltages.